1.3 Purpose of this User Manual
1.4 Who Should Use This Manual
1.4 Best Practices and System Limitations
1.4.1 Setting up the Master Files
4.1.1.1 How to Add an Item Manually
4.1.1.2 Add Item Via Import Function
4.1.2.2 Add Customer Via Import Function
4.1.3.2 Add Supplier Via Import Function
List of All Users that were added to the System
4.1.6.1 Chart of Accounts Lists
4.1.6.2 Manual Add Chart of Accounts
4.1.6.2 Add Chart of Accounts via Upload Account
4.1.8.2 Manual Add of Currency
4.2.1.1 Manual Update Item Detail
4.2.1.2 Update Item Detail in Bulk
4.2.2.1 Manual Update Supplier Detail
4.2.2.1 Update Supplier Detail in Bulk
4.2.3.1 Manual Update Customer Detail
4.2.3.1 Update Customer Detail in Bulk
5.2 Purchases Transaction Module
Cancel Purchase Request Transaction
Purchase Order Transaction via Upload Template
Cancel Purchase Order Transaction
Cancel Receiving Receipt Transaction
Cancel Disbursement Transaction
Debit Memo Transaction via Upload Template
Sales Order Transaction via Upload Template
Cancel Sales Order Transaction
Sales Invoice Transaction via Upload Template
Cancel Sales Invoice Transaction
Collection Transaction via Upload Template
Scenario 3: Extra-Ordinary Activities
Scenario 4: Multi-Branch with EasyPOS Integration
Accounts Payable Voucher Report
Accounts Payable By Currency Report
Purchase Request Summary Report
Purchase Request Detail Report
Purchase Order Detail With Balance Report
Receiving Receipt Summary Report
Receiving Receipt Detail Report
Print or Download the PDF Report
Available Item Per Batch Report
Cancelled Purchase Request Report
Cancelled Purchase Order Report
Cancelled Receiving Receipt Report
Accounts Receivable Summary Report
Accounts Receivable by Term Report
Accounts Receivable by Currency Report
Accounts Receivable Report (One Month)
Statement of Account (By Date Range)
Collection Summary by PayType Report
Cancelled Sales Invoice Report
Sales Invoice Detail Report with Cost
Stock Transfer Detailed Report
13.1.1 Benefits of Integration
13.2.1 EasyPOS Integration Overview
13.3 How to Set Up Integrations
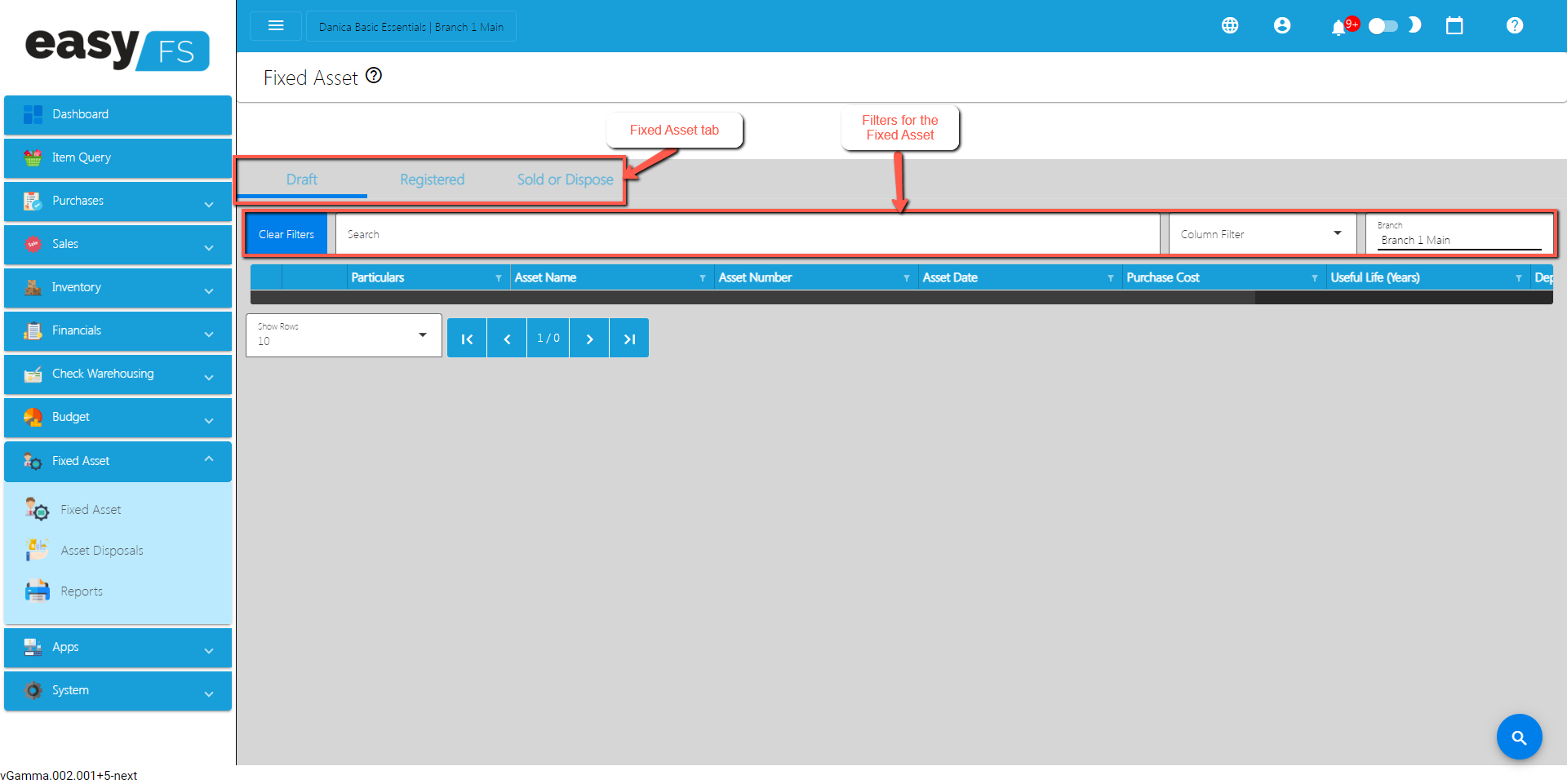
.toc-wrapper .c27{margin-left: 6pt}.toc-wrapper .c46{margin-left:14pt}.toc-wrapper .c46 .c14 a,.toc-wrapper .c50 a{font-size:13px}.toc-wrapper .c50{margin-left:18pt;} .manual-content table td, .manual-content table th{padding:0;border: 1px #aaa solid;padding: 10px;} .manual-content table td span,.manual-content table td p,.manual-content table td li{font-size:11px!important;}EasyFS Fixed Asset, also known as a Fixed Asset Ledger or Fixed Asset Schedule, is a detailed record that systematically tracks and manages an organization’s fixed assets. Fixed assets are long-term, tangible assets with a useful life of more than one accounting period. Examples include buildings, machinery, vehicles, furniture, and land.
The Fixed Asset Register serves several purposes:
Asset Registration: It provides a unique identification for each fixed asset, typically through an asset tag or serial number. This helps in easy identification and tracking.
Description and Details: The register includes detailed information about each fixed asset, such as its description, location, acquisition date, purchase cost, depreciation method, salvage value, and useful life.
Cost and Valuation: The register records the original cost of acquiring the asset, any subsequent improvements or additions, and the current valuation. This information is crucial for financial reporting and tax purposes.
Depreciation: For assets subject to depreciation (the allocation of the asset’s cost over its useful life), the register includes details on the depreciation method used, the rate of depreciation, and the accumulated depreciation to date.
Maintenance and Repairs: It may include records of maintenance activities, repairs, and any upgrades or improvements made to the fixed asset.
Location Changes: If a fixed asset is moved within the organization, the register is updated to reflect the new location.
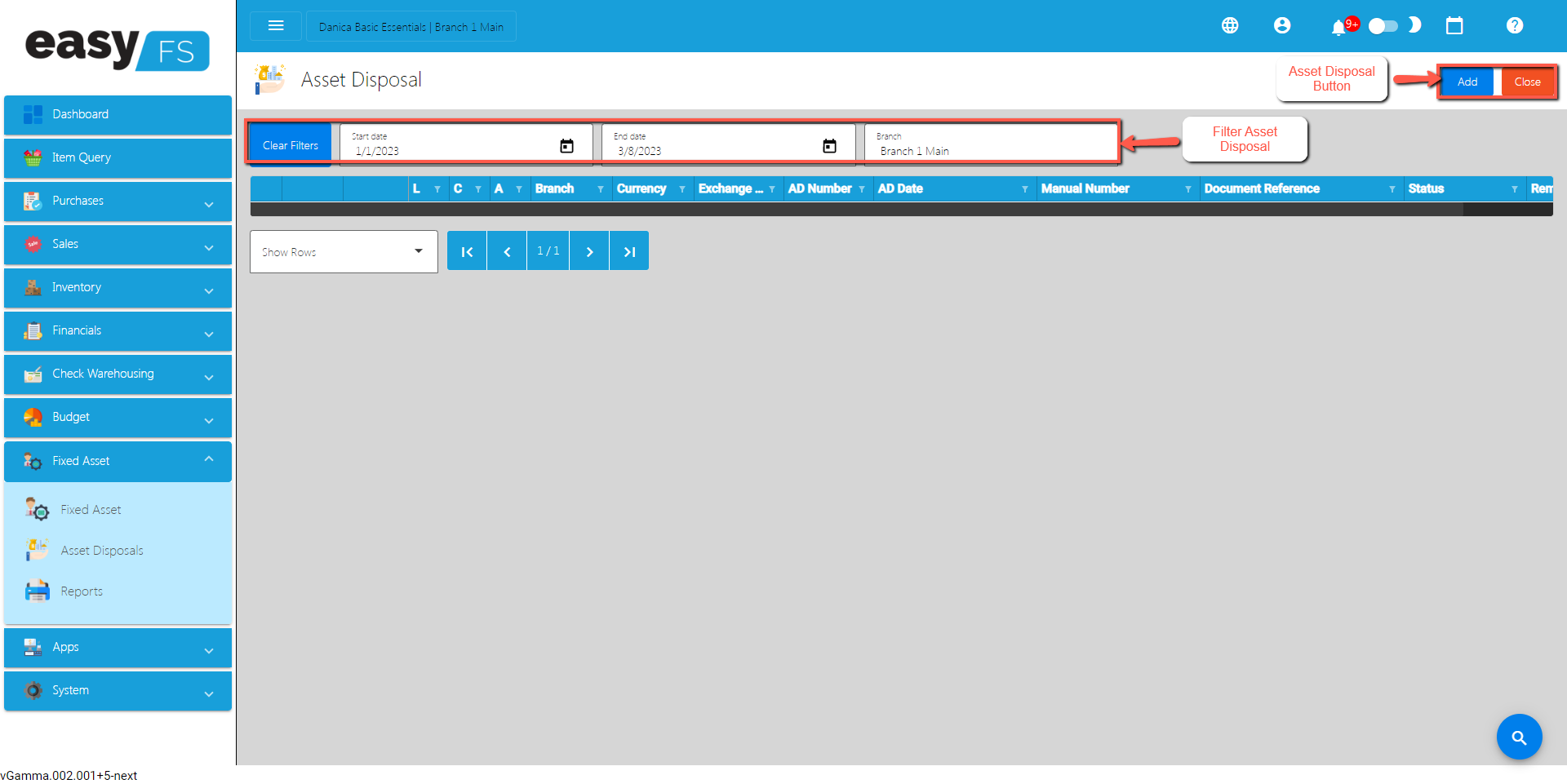
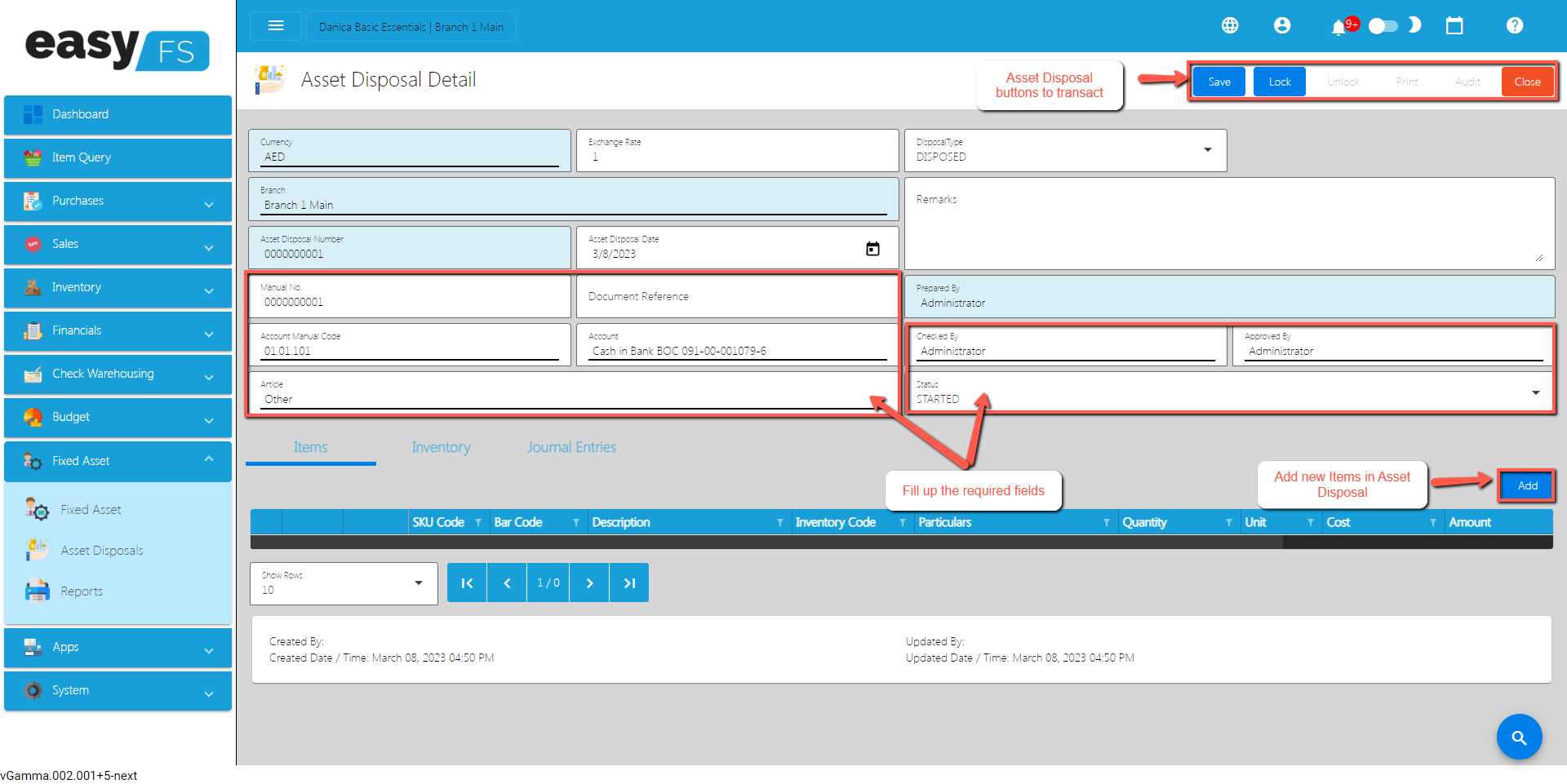
Disposal: When a fixed asset is disposed of or sold, details of the disposal, including the date, selling price, and reason for disposal, are recorded in the register.
Compliance: The Fixed Asset Register helps in complying with accounting standards and regulatory requirements related to the reporting and management of fixed assets.
Insurance: It aids in managing insurance coverage by providing accurate information about the value and location of fixed assets.
The Fixed Asset Register is a critical tool for financial management, accounting, and asset tracking. It helps organizations make informed decisions about their asset portfolio, assess the financial impact of fixed asset transactions, and maintain accurate records for financial reporting and auditing purposes.

Typically replies within a few hours
 Log in to Messenger
Log in to Messenger
